The hidden world of deep-sea creatures is nothing short of mesmerizing. Imagine anglerfish using glowing lures to attract prey, or gulper eels gulping down meals with their enormous mouths. You'll be amazed by how animals like the vampire squid thrive in low oxygen while giant isopods scavenge on the ocean floor. These fascinating adaptations and unique feeding strategies help them survive in extreme environments. Plus, bioluminescence shines a light on their mysterious world, aiding in communication and survival. This is just the tip of the iceberg—there's so much more to uncover about these incredible beings.
Key Takeaways
- Deep-sea creatures like the anglerfish use bioluminescence to attract prey, showcasing unique adaptations for survival in dark environments.
- The gulper eel's massive mouth allows it to consume prey significantly larger than itself, highlighting extreme feeding strategies in the deep sea.
- Diverse species such as giant isopods and vampire squids exhibit remarkable resilience, scavenging and thriving in nutrient-scarce ecosystems.
- Technological innovations like ROVs and AUVs are unveiling new species and ecosystems, revolutionizing our understanding of deep-sea life.
- Deep-sea ecosystems are critical for marine biodiversity, yet face threats from climate change and human activity, necessitating urgent conservation efforts.
Fascinating Adaptations of Deep-Sea Creatures

When you explore the depths of the ocean, you'll discover that deep-sea creatures have evolved some truly fascinating adaptations to survive in their extreme environment.
Take the anglerfish, for instance; its bioluminescent lure attracts prey in dark waters, thanks to symbiotic bacteria.
The gulper eel can gobble up prey half its size, with its massive mouth making up 25% of its length, perfect for food-scarce surroundings.
The long-nosed chimaera, or "ghost shark," utilizes its unique snout filled with sensory nerve endings for effective hunting in darkness.
Meanwhile, the dumbo octopus thrives at 4,000 meters deep without an ink sac, and giant isopods scavenge on dead matter, showcasing remarkable resilience.
These adaptations highlight nature's ingenuity in challenging conditions.
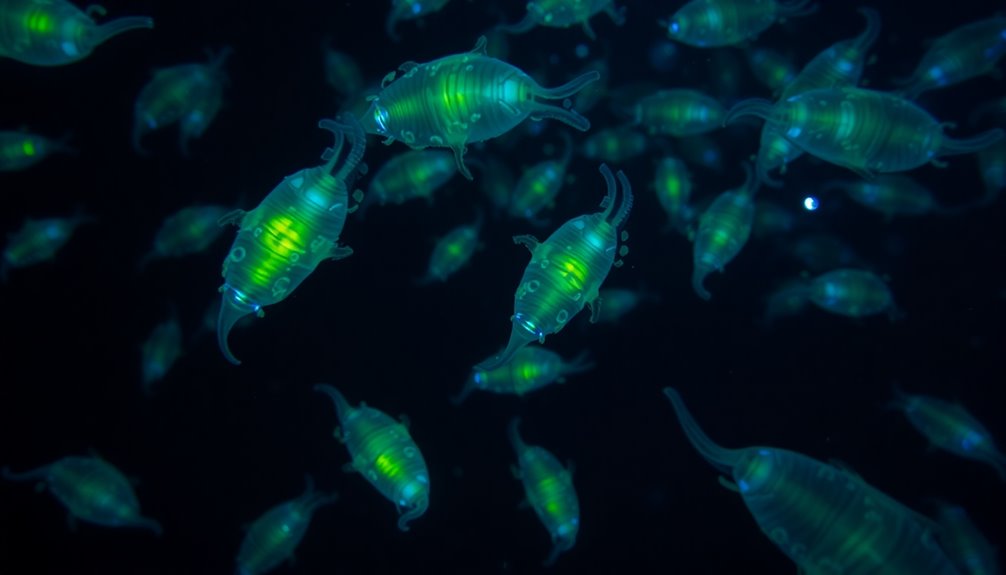
Bioluminescence: Nature's Underwater Lights

As you explore the mysterious world of the deep sea, you'll encounter bioluminescence—a fascinating phenomenon that illuminates the darkness. This natural light show serves various purposes for deep-sea creatures, particularly in attracting bioluminescent prey.
Here are some enthralling examples:
- The Deep Sea Angler Fish uses a bioluminescent lure from symbiotic bacteria to entice its meals.
- Gulper Eels emit light from their tails to attract small crustaceans.
- Many jellyfish use glowing tentacles for communication and capturing prey.
- The Bloodybelly Comb Jelly dazzles with its crimson, sparkling display.
- Bioluminescence also helps species attract mates and deter predators.
In this enchanting underwater world, light isn't just for show; it's essential for survival.
Unique Feeding Strategies Explored

Deep-sea creatures have evolved a variety of unique feeding strategies to thrive in their dark, nutrient-scarce environment. For instance, the anglerfish uses a bioluminescent lure to attract prey, while the vampire squid feeds on marine detritus. In contrast, giant isopods scavenge dead animals, contributing to nutrient recycling. Each of these strategies allows them to maximize their chances of survival.
| Creature | Feeding Strategy | Unique Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Anglerfish | Uses bioluminescent lure | Attracts prey in darkness |
| Vampire Squid | Feeds on marine detritus | Adapted to low oxygen |
| Giant Isopod | Scavenges on dead animals | Nutrient recycling |
| Gulper Eel | Scoops up crustaceans | Massive mouth |
The Role of Deep-Sea Ecosystems

The fascinating feeding strategies of deep-sea creatures highlight the complexity of their habitats. Deep-sea ecosystems cover over 65% of the Earth's surface, hosting unique species adapted to extreme conditions.
These ecosystems play a vital role in nutrient recycling, contributing to the health of the deep ocean.
- Hydrothermal vents support life through chemosynthesis.
- Organisms like sea cucumbers and giant isopods scavenge dead matter.
- Bioluminescent creatures, such as anglerfish, use light for communication.
- The deep-sea food web relies on organic matter from the surface.
- New species discoveries emphasize the need for conservation.
Understanding these roles deepens your appreciation for the interconnectedness of marine ecosystems and underscores the fragility of these hidden habitats.
Recent Discoveries in Ocean Depths

You won't believe the incredible new species being uncovered in the ocean's depths!
Recent expeditions have revealed unique adaptations among these creatures, showcasing nature's ingenuity.
Plus, advancements in exploration techniques are making it easier than ever to discover what lies beneath the surface.
New Species Discoveries
As researchers dive deeper into the ocean's uncharted territories, exciting discoveries continue to emerge, revealing a wealth of new species.
In 2022 alone, an expedition in the Clarion-Clipperton Zone uncovered 55 species, with at least 39 new to science. This highlights the astonishing biodiversity lurking in unexplored depths.
Here's a glimpse of recent new species discoveries:
- A slickhead fish in Suruga Bay, measuring 1.4 meters and weighing 25 kilograms.
- Unique tube worms that challenge biological classifications.
- Yeti crabs, showcasing the ocean's oddities.
- Evidence suggesting current exploration methods might be inadequate.
- Fewer than 250,000 species identified out of an estimated 2 million in the oceans.
These findings remind us of the mysteries the deep-sea creatures still hold.
Unique Adaptations Observed
While exploring the ocean's depths, researchers have uncovered remarkable adaptations that enable deep-sea creatures to thrive in extreme environments.
For instance, the Gulper Eel boasts a massive mouth that can extend to scoop prey twice its size, making up about 25% of its body length.
The Deep Sea Angler Fish employs a bioluminescent lure, attracting prey in the pitch-black waters using symbiotic bacteria.
Long-Nosed Chimaeras, known as "ghost sharks," have sensitive snouts filled with nerve endings that help them hunt effectively in darkness.
Dumbo Octopuses have adapted to lack an ink sac, using their ear-like fins for propulsion instead.
Finally, the Giant Seed Shrimp's body is 95% water, with large eyes tailored for detecting bioluminescent prey in the deep ocean.
Exploration Techniques Advancements
Recent advancements in underwater exploration techniques have revolutionized our ability to uncover the mysteries of the deep ocean.
You'd be amazed at how these innovations enhance our understanding of deep-sea life.
- Submersibles and ROVs enable the discovery of new species.
- High-resolution mapping tools offer insights into unknown ecosystems.
- Infrared light techniques help track elusive deep-sea creatures.
- Hybrid devices attract predators to study feeding strategies.
- Recent expeditions in the Clarion-Clipperton Zone revealed 55 new species, 39 of which are entirely new to science.
These exploration techniques not only illuminate the depths but also highlight the importance of ongoing research in our quest to understand the vast, hidden world beneath the waves.
Conservation Challenges and Solutions

Despite the vastness of the deep sea, its unique ecosystems face significant conservation challenges that demand immediate attention. Human activities like deep-sea mining threaten these fragile habitats. With an estimated 1.75 million undiscovered species at risk, effective environmental regulations are vital. Vulnerable species, such as the Sea Angel and Flapjack Octopus, suffer from climate change and ocean acidification.
| Conservation Challenge | Impact | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Deep-Sea Mining | Habitat destruction | Enforce strict regulations |
| Climate Change | Species vulnerability | Promote global climate action |
| Lack of Research | Informed policies lacking | Increase funding for exploration |
International collaboration and innovative exploration techniques are essential to understanding and preserving these ecosystems.
Technological Advances in Exploration
You're witnessing a revolution in deep-sea exploration thanks to Remote Operated Vehicles (ROVs) and Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs).
These technologies enable you to explore uncharted depths and gather high-resolution data about the ocean floor like never before.
With advanced mapping tools, you can uncover the secrets of deep-sea habitats and enhance your understanding of these mysterious environments.
Remote Operated Vehicles
As scientists push the boundaries of ocean exploration, Remote Operated Vehicles (ROVs) play an essential role in uncovering the mysteries of the deep sea.
These remarkable machines allow you to witness the ocean's wonders from afar, equipped with advanced cameras and sensors that capture high-resolution images at depths of up to 6,000 meters.
Here's what sets ROVs apart:
- Remotely controlled from research ships
- Equipped with manipulators for specimen collection
- Capable of exploring extreme environments
- Enable high-definition video footage for research
- Pave the way for autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs)
Thanks to remote operated vehicles, your understanding of deep-sea biodiversity and behaviors expands, revealing the secrets of the ocean's hidden inhabitants.
High-Resolution Mapping Tools
Remote Operated Vehicles have paved the way for new exploration techniques, especially in mapping the ocean floor.
High-resolution mapping tools, like multibeam sonar systems, let you create detailed topographic maps that reveal underwater features and habitats previously unknown. These advanced techniques enhance your ability to explore vast areas of the ocean more efficiently than traditional methods.
By integrating satellite technology with underwater mapping, you gain insights into oceanic currents and their effects on deep-sea ecosystems.
Additionally, recent advancements in imaging technology allow you to capture high-definition video footage of elusive deep-sea creatures, offering valuable insights into their behavior and ecology.
This combination of technologies transforms how we perceive and navigate the hidden depths of our oceans.
Autonomous Underwater Vehicles
Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) are revolutionizing deep-sea exploration by operating independently at depths greater than 6,000 meters.
These advanced robotic systems survey vast ocean areas without human intervention, making significant contributions to our understanding of the deep ocean.
Here's what you should know about AUVs:
- They use sonar and high-resolution cameras for 3D mapping of the ocean floor.
- Equipped with sensors, they collect data on temperature, salinity, and biological samples.
- AUVs help discover new marine species and ecosystems.
- They enable real-time studies of deep-sea ecosystems.
- Prolonged missions reduce risks associated with manned exploration.
With AUVs, the mysteries of the deep ocean are slowly unraveling, enhancing our knowledge of underwater life.
The Mystery of Unidentified Species

What secrets lie beneath the ocean's surface? You might be surprised to learn that an estimated 2 million species call the oceans home, yet fewer than 250,000 have been identified. This leaves a staggering number of unidentified species lurking in the deep, waiting to be discovered.
The deep sea, which makes up about 99.5% of Earth's habitats, remains largely unexplored. Recent expeditions have disclosed incredible biodiversity, including 55 species found in the Clarion-Clipperton Zone, with 39 completely new to science.
Innovative techniques, like infrared light tracking, are essential for revealing these elusive organisms. With deep-sea ecosystems taking decades to recover from disturbances, it's urgent to document and protect the astonishing biodiversity that still lies hidden in the depths.
Impacts of Deep-Sea Mining

When you consider deep-sea mining, you can't ignore the risks it poses to fragile ecosystems and the potential for significant biodiversity loss.
Regulatory challenges are already complicating efforts to protect these uncharted territories, raising concerns about the long-term impacts of extraction.
It's essential to think about how these activities could disrupt the delicate balance of marine life.
Ecological Disruption Risks
Though deep-sea mining promises economic benefits, it poses serious ecological disruption risks that can lead to long-lasting damage.
The unique ecosystems of the deep ocean are incredibly fragile, and mining activities can devastate them. Historical data shows that these ecosystems may take decades to recover, if they recover at all.
Here are some key concerns regarding ecological disruption risks:
- Destruction of unique habitats like hydrothermal vents
- Challenges in regulating mining practices effectively
- Potential for irreversible damage to ecosystems
- Struggles of affected ecosystems to recover after disturbances
- Urgent need for protective measures before exploitation begins
Understanding these risks is essential for safeguarding the deep ocean's remarkable biodiversity and ensuring that we don't lose these critical habitats forever.
Biodiversity Loss Concerns
As deep-sea mining operations ramp up, the threat to biodiversity in these unexplored ecosystems becomes increasingly alarming.
Historical data shows that disturbances can take decades for these environments to recover. With the International Seabed Authority under pressure to establish regulations, unique habitats risk destruction before they can even be studied.
Recent investigations have uncovered previously unknown ecosystems that could be severely impacted by mining, reinforcing the need for exploration to support conservation efforts.
The long-term effects of deep-sea mining on biodiversity remain uncertain, but the potential loss is staggering, with estimates suggesting up to 1.75 million undiscovered species may inhabit these depths.
Protecting these uncharted territories is essential to prevent irreversible biodiversity loss.
Regulatory Challenges Ahead
The urgency of protecting deep-sea ecosystems is underscored by the regulatory challenges posed by increasing mining activities.
Nauru's push for deep-sea mining has triggered critical discussions, as the International Seabed Authority races against time to establish necessary regulations.
Without these rules, unique marine life could face destruction before we even understand their ecosystems.
- Significant risk of biodiversity loss
- Decades needed for recovery of affected habitats
- Threat to specialized species in hydrothermal vents
- Lack of thorough exploration complicates assessments
- Urgent need for effective environmental regulations
These regulatory challenges ahead highlight the precarious balance between resource extraction and the preservation of deep-sea environments that remain largely uncharted and vulnerable.
Future of Deep-Ocean Research

While the deep ocean remains an enigma, the future of deep-ocean research promises to reveal its secrets through technological innovation and international collaboration.
With only a tiny fraction of the deep-sea ecosystems mapped, the urgency for exploration has never been greater. Advances in submersibles, remotely operated vehicles (ROVs), and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) are revolutionizing how you discover new species and understand deep-sea habitats.
Collaborative efforts are essential, as a unified approach will enhance surveys and boost public interest in oceanography. Additionally, securing funding for research and education supports innovative tools and methods vital for uncovering the mysteries of the deep sea.
Integrating satellite technology will further enrich your understanding of these remarkable ecosystems and their biodiversity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Lives at 13,000 Feet Underwater?
At 13,000 feet underwater, you'll discover fascinating creatures like the Dumbo Octopus, which uses its ear-like fins to glide through the depths.
You might encounter the Giant Squid, known for its impressive size and large eyes, perfect for the dark environment.
Don't forget about bioluminescent jellyfish that light up the abyss, and unique organisms around hydrothermal vents, including tube worms and extremophilic bacteria, thriving in extreme conditions.
What Is the Most Terrifying Deep Sea Creature?
When you think of terrifying deep-sea creatures, the Deep Sea Anglerfish, Goblin Shark, and Giant Squid instantly come to mind.
The Anglerfish uses its bioluminescent lure to attract unsuspecting prey, while the Goblin Shark's extendable jaw snaps up its dinner with eerie efficiency.
Then there's the Giant Squid, a fierce predator that battles sperm whales.
Each of these creatures thrives in darkness, showcasing nature's ability to create both beauty and fear beneath the waves.
What Was Found in the Ocean in 2024?
In 2024, you'd be amazed to learn that researchers discovered a new slickhead fish in Suruga Bay, measuring 1.4 meters and weighing 25 kilograms.
An expedition in the Clarion-Clipperton Zone identified 55 new species, including at least 39 completely new to science, like tube worms and Yeti crabs.
These findings highlight the need for better exploration methods to understand deep-sea biodiversity and emphasize the urgency for conservation efforts.
Are There Undiscovered Deep Sea Creatures?
Did you know that an estimated 2 million species might inhabit the oceans, yet we've only identified fewer than 250,000? This highlights that there are indeed countless undiscovered deep-sea creatures waiting to be explored.
Recent expeditions have uncovered new species, but many smaller organisms remain unaccounted for.
With innovative techniques, you can help reveal the mysteries of these ecosystems, emphasizing the need to protect them before it's too late.
Conclusion
As you dive deeper into the hidden world of deep-sea creatures, you uncover a vibrant tapestry of life that's as mysterious as it is mesmerizing. Each adaptation sparkles like stars in an abyss, revealing nature's ingenuity. Yet, the shadows hold secrets, with many species still waiting to be discovered. Embracing the unknown, we must tread carefully, for the depths are a fragile wonderland, inviting us to explore while reminding us to protect its breathtaking beauty for generations to come.








